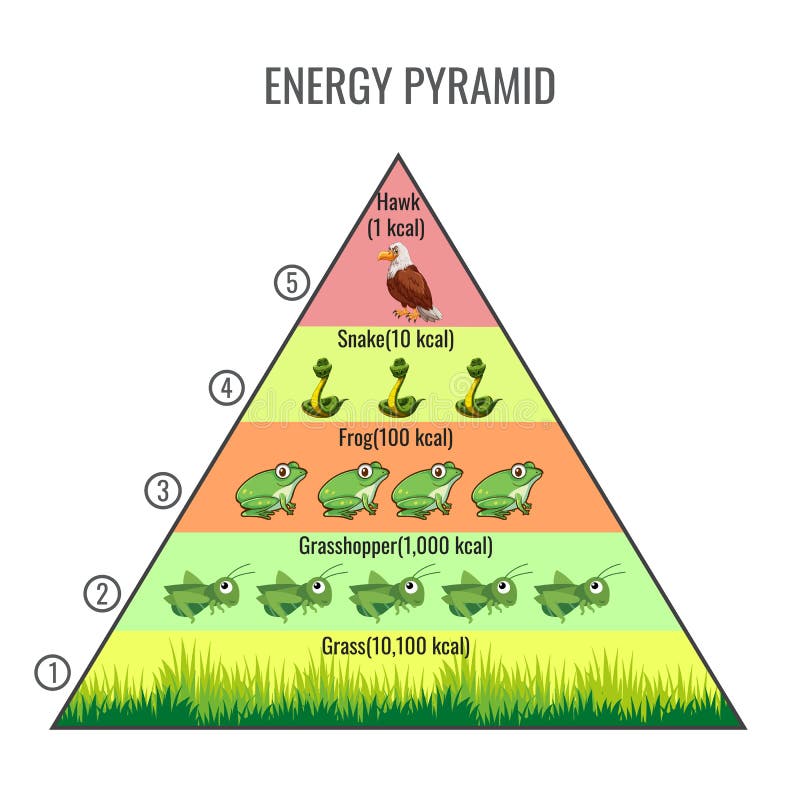
Food Pyramid Ecosystem Biology Diagrams Learn about the concept of trophic level, the position of organisms in a food chain or a food web, and the energy flow within an ecosystem. Find out the types of food chains, food webs, and trophic level pyramids with examples and diagrams.

A food web is a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. Learn how food webs are structured by trophic levels, producers, consumers, detritivores, and decomposers, and how they differ from food chains. trophic pyramid, the basic structure of interaction in all biological communities characterized by the manner in which food energy is passed from one trophic level to the next along the food chain. The base of the pyramid is composed of species called autotrophs, the primary producers of the ecosystem. Learn about the different types of ecological pyramids that show the biomass, productivity, or numbers of organisms at each trophic level in an ecosystem. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of each pyramid and see examples of upright, inverted, or spindle-shaped pyramids.

Definition, Examples, and Diagram Biology Diagrams
Students copy the pyramid on their paper. Using the food chain examples in step 1, walk the students through placing these organisms within the pyramid. The added feature to the energy pyramid is the inclusion of arrows depicting the flow of energy. By showing the trophic (feeding) levels of the ecosystem, students can easily visualize how

Learn about the five trophic levels in a food chain and how they represent energy flow and biomass. Find out which organisms are producers, consumers, and decomposers and how they interact in an ecological pyramid. Learn about the structure and function of food chains and food webs in ecology. Explore the concepts of trophic levels, energy transfer, biomagnification, and top-down and bottom-up control in ecosystems. Trophic level is a step in a food chain of an ecosystem, based on feeding behavior. Learn about the four levels of producers, herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers, and how they interact in an ecosystem.